Chloethompson
On this page, you find all documents, package deals, and flashcards offered by seller ChloeThompson.
- 82
- 0
- 0
Community
- Followers
- Following
2 Reviews received
82 items

Anatomy of the Muscular System: Introduction & Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Trunk
Anatomy of the Muscular System: Introduction & Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Trunk. Sternocleidomastoid Origin: Sternal end of clavicle and manubrium Insertion: Mastoid region of skull Action: Bilateral: Neck flexion Unilateral: Turns face to opposite side Innervation: Accessory nerve (CN XI) Splenius Capitis Origin: Spinous process/ligaments of inferior cervical vertebrae Insertion: Mastoid process, occipital bones of skull Action: Bilateral extend head Unilateral laterally fle...
- Class notes
- • 221 pages •
Anatomy of the Muscular System: Introduction & Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Trunk. Sternocleidomastoid Origin: Sternal end of clavicle and manubrium Insertion: Mastoid region of skull Action: Bilateral: Neck flexion Unilateral: Turns face to opposite side Innervation: Accessory nerve (CN XI) Splenius Capitis Origin: Spinous process/ligaments of inferior cervical vertebrae Insertion: Mastoid process, occipital bones of skull Action: Bilateral extend head Unilateral laterally fle...

BIOL 3V2 Exam 1 study guide
BIOL 3V2 Exam 1 study guide 1. Describe the system of nomenclature (i.e. naming and writing the names) of microorganisms. Should be written: Genus species or if hand written Genus species. Can be abbreviated if the 2nd time written and on (ex. G. species) 2. Describe the characteristics of each of the following: bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, and algae. Focus on distinguishing features that were discussed in class. • Bacteria: unicellular, prokaryote, CW: peptidoglycan, binary fiss...
- Other
- • 9 pages •
BIOL 3V2 Exam 1 study guide 1. Describe the system of nomenclature (i.e. naming and writing the names) of microorganisms. Should be written: Genus species or if hand written Genus species. Can be abbreviated if the 2nd time written and on (ex. G. species) 2. Describe the characteristics of each of the following: bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, and algae. Focus on distinguishing features that were discussed in class. • Bacteria: unicellular, prokaryote, CW: peptidoglycan, binary fiss...

BIOL 3V2 Exam 2 study guide
BIOL 3V2 Exam 2 study guide 1. Understand the difference between physical requirements for growth and chemical requirements for growth. 2. What are the physical factors that affect microbial growth? What are the chemical factors? 3. Be able to classify microbes on the basis of preferred temperature range. 4. Be able to classify microbes based on their preferred pH range. Which is most common? 5. Explain how osmotic pressure can effect microbial growth. 6. Be able to relate temperature ...
- Other
- • 6 pages •
BIOL 3V2 Exam 2 study guide 1. Understand the difference between physical requirements for growth and chemical requirements for growth. 2. What are the physical factors that affect microbial growth? What are the chemical factors? 3. Be able to classify microbes on the basis of preferred temperature range. 4. Be able to classify microbes based on their preferred pH range. Which is most common? 5. Explain how osmotic pressure can effect microbial growth. 6. Be able to relate temperature ...

Exam (elaborations) Biology
BIOL 2450 Exam (elaborations) Biology 1. Which of the following birth control methods is a “barrier” method? b) diaphragm 2. Which of the following chemicals signals the body that the egg has been fertilized: c) human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) 3. Which of the following occurs in fertilization: c) only the sperm nucleus enters 4. The part of the male reproductive system that adds fructose and prostaglandins to the semen is the: d) seminal vesicle 5. Which of ...
- Exam (elaborations)
- • 42 pages •
BIOL 2450 Exam (elaborations) Biology 1. Which of the following birth control methods is a “barrier” method? b) diaphragm 2. Which of the following chemicals signals the body that the egg has been fertilized: c) human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) 3. Which of the following occurs in fertilization: c) only the sperm nucleus enters 4. The part of the male reproductive system that adds fructose and prostaglandins to the semen is the: d) seminal vesicle 5. Which of ...

Cell Energy Cycle
M4 L2 Gizmo Simulation: Cell Energy Cycle 1. What does a plant need to survive and grow? Water air sun 2. What does an animal need to survive and grow? Water food shelter 3. How do animals and plants depend on each other? Animals eat the food and the plants grow off of it
- Exam (elaborations)
- • 11 pages •
M4 L2 Gizmo Simulation: Cell Energy Cycle 1. What does a plant need to survive and grow? Water air sun 2. What does an animal need to survive and grow? Water food shelter 3. How do animals and plants depend on each other? Animals eat the food and the plants grow off of it

M6L2 Gizmo Lab: Cell Division
M6L2 Gizmo Lab: Cell Division Cells reproduce by splitting in half, a process called cell division. What do cells need to do between divisions to make sure that they don’t just get smaller and smaller? Based on these two observations, would you say that a cell spends most of its life cycle in interphase or in mitosis/cytokinesis?
- Class notes
- • 12 pages •
M6L2 Gizmo Lab: Cell Division Cells reproduce by splitting in half, a process called cell division. What do cells need to do between divisions to make sure that they don’t just get smaller and smaller? Based on these two observations, would you say that a cell spends most of its life cycle in interphase or in mitosis/cytokinesis?
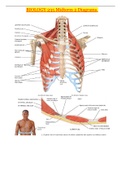
BIOLOGY 235 Midterm 2 Diagrams
BIOLOGY 235 Midterm 2 Diagrams Fibrous tunic [Pronunciation] Cornea: Admits and refracts (bends) light. Sclera: Provides shape and protects inner parts. Vascular tunic [Pronunciation] Iris: Regulates amount of light that enters eyeball. Ciliary body: Secretes aqueous humor and alters shape of lens for near or far vision (accommodation). Choroid: Provides blood supply and absorbs scattered light. Retina [Pronunciation] Receives light and converts it into receptor potentia...
- Class notes
- • 51 pages •
BIOLOGY 235 Midterm 2 Diagrams Fibrous tunic [Pronunciation] Cornea: Admits and refracts (bends) light. Sclera: Provides shape and protects inner parts. Vascular tunic [Pronunciation] Iris: Regulates amount of light that enters eyeball. Ciliary body: Secretes aqueous humor and alters shape of lens for near or far vision (accommodation). Choroid: Provides blood supply and absorbs scattered light. Retina [Pronunciation] Receives light and converts it into receptor potentia...

BIOLOGY 235 MIDTERM 2 REVIEW CHAPTER 11: THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
BIOLOGY 235 MIDTERM 2 REVIEW CHAPTER 11: THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM origin - stationary bone, usually proximal Insertion - attachment of muscle's other tendon to movable bone, usually distal belly (body) - fleshy portion of muscle between their tendons (origin and insertion) Actions - main movements that occur when the muscle contracts reverse muscle action (RMA) - during specific movements the actions are reversed; • bones act as levers, and joints function as the fulcrums o...
- Class notes
- • 118 pages •
BIOLOGY 235 MIDTERM 2 REVIEW CHAPTER 11: THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM origin - stationary bone, usually proximal Insertion - attachment of muscle's other tendon to movable bone, usually distal belly (body) - fleshy portion of muscle between their tendons (origin and insertion) Actions - main movements that occur when the muscle contracts reverse muscle action (RMA) - during specific movements the actions are reversed; • bones act as levers, and joints function as the fulcrums o...

M5 L1: Gizmo Lab Building DNA
M5 L1: Gizmo Lab Building DNA Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) DNA is an incredible molecule that forms the basis of life on Earth. DNA molecules contain instructions for building every living organism on Earth, from the tiniest bacterium to a massive blue whale. DNA also has the ability to replicate, or make copies of itself. This allows living things to grow and reproduce. 1. Look at the DNA molecule shown at right. What does it look like? This shape is called...
- Class notes
- • 9 pages •
M5 L1: Gizmo Lab Building DNA Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) DNA is an incredible molecule that forms the basis of life on Earth. DNA molecules contain instructions for building every living organism on Earth, from the tiniest bacterium to a massive blue whale. DNA also has the ability to replicate, or make copies of itself. This allows living things to grow and reproduce. 1. Look at the DNA molecule shown at right. What does it look like? This shape is called...

BIOS 256 Final Exam Study Guide 2020
BIOS 256 Final Exam Study Guide 2020 1 The urinary system does all of the following, EXCEPT it A secretes excess glucose molecules B regulates blood volume C contributes to stabilizing blood pH D eliminates organic waste products E regulates plasma concentrations of electrolytes 2 Conical structures that are located in the renal medulla are called A pyramids B renal columns C renal pelvises D nephrons E calyces 3 The region known as the macula densa is part of A the ...
- Exam (elaborations)
- • 24 pages •
BIOS 256 Final Exam Study Guide 2020 1 The urinary system does all of the following, EXCEPT it A secretes excess glucose molecules B regulates blood volume C contributes to stabilizing blood pH D eliminates organic waste products E regulates plasma concentrations of electrolytes 2 Conical structures that are located in the renal medulla are called A pyramids B renal columns C renal pelvises D nephrons E calyces 3 The region known as the macula densa is part of A the ...

PHSC 211 Chapter 4 Quiz (Fall 2020)
TEST BANK FOR POPULATION HEALTH IN COMMUNITY PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING 5TH EDITION STANHOPE CHAPTER 1-32