Types of nucleation - Study guides, Class notes & Summaries
Looking for the best study guides, study notes and summaries about Types of nucleation? On this page you'll find 36 study documents about Types of nucleation.
Page 4 out of 36 results
Sort by
-
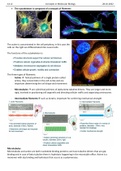
The cytoskeleton is composed of a network of filaments
- Class notes • 17 pages • 2022
-
- $9.26
- + learn more
The actine is concentrated in the cell periphery, in this case the cells on the right are differentiated into neural cells. The functions of the cytoskeleton is: The three types of filaments: - Actine helical polimers of a single protein called actine, they concentrate in the cell cortex and are important determining the cell shape and movement - Microtubules are cylindrical polimers of alpha-beta tubuline dimers. They are larger and more rigid, involved in positioning cell org...

-
NUR 2063 Pathophysiology Exam 2 questions correctly answered latest 2022
- Exam (elaborations) • 17 pages • 2022
- Available in package deal
-
- $11.99
- + learn more
NUR 2063 Pathophysiology Exam 2 questions correctly answered latest 2022What is gastritis? Inflammation of the stomach lining. The lining will be red and inflamed and irritated What are the causes of gastritis? Ingestion of irritating substances such a alcohol, aspirin, NSAIDS, viruses and bacteria What is GERD? the back flow of gastric contents into the esophagus through the lower esophageal sphincter. The inflammation occurs from the reflex of highly acidic stomach acid that c...

-
NUR2063/PATHOPHYSI NUR2063 SE Essentials of Pathophysiology - Exam 2 review sheet 2021
- Exam (elaborations) • 7 pages • 2021
- Available in package deal
-
- $12.99
- + learn more
NUR2063/PATHOPHYSI NUR2063 SE Essentials of Pathophysiology - Exam 2 review sheet 2021 ⦁ What is gastritis? What are causes? - inflammation of the stomach lining, pain in LUQ, causes- irritation due to medication, alcohol, caffeine. Signs and symptoms stomach pain, nausea, vomiting and bloating. ⦁ What is GERD? What are causes to this condition? What are complications of GERD if left untreated? Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease- backflow of gastric content into esophagus through lower e...

-
Principles of epitaxy
- Class notes • 10 pages • 2022
-
- $9.49
- + learn more
Principles of epitaxy Kinetics of Epitaxial Growth Surface Diffusion and NucleationTypes of Interfaces coherent, semi-coherent, and incoherentKinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component Systemgeneral kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximationKinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System description of diffusion flux across the αβ interfaceKinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System dilute solution approximationRate of NucleationHeterogeneous Nucleation a surface ...

-
Exam (elaborations) BIO 353/BIO353 (BIO353) BIO353: Exam 2 Short Answers | BIO 353 Exam 2 Short Answered
- Exam (elaborations) • 17 pages • 2022
-
- $17.49
- + learn more
BIO353: Exam 2 Short Answers Module 11: Actin Filaments 1. Draw an actin monomer and an actin filament and label all the parts, molecular weights, etc.. 2. Explain the geography of actin filaments. Explain the geography of stress cable, filapodia and lamelliapodia in a cell, and locomoting in a culture plate. 3. Focusing on actin monomers and actin filaments: explain what occurs when a cell reverses its direction by 180 degrees. 4. Explain how the binding of ATP affects cytoskeletal monomers. Ex...

-
NUR 2063 Pathophysiology Exam 3 Review Complete & Latest Update
- Exam (elaborations) • 52 pages • 2021
-
- $18.49
- + learn more
NUR 2063 Pathophysiology Exam 3 Review Complete Primary Brain Injury: occurs as a direct result of the initial insult Secondary Brain Injury: progressive damage resulting from the body’s physiological response to the initial insult Reperfusion Injury: occurs when blood flow is reintroduced to previously ischemic but viable cells. Free radicals are generated, which damage cell structures. Inflammatory cells are recruited to the area and may increase edema, blood vessels, and contribute t...

Do you wonder why so many students wear nice clothes, have money to spare and enjoy tons of free time? Well, they sell on Stuvia! Imagine your study notes being downloaded a dozen times for $15 each. Every. Single. Day. Discover all about earning on Stuvia


