Alexanorton
On this page, you find all documents, package deals, and flashcards offered by seller alexanorton.
- 11
- 0
- 0
Community
- Followers
- Following
11 items

Behavioral Ecology
There are four levels of analysis for questions addressing animal behavior. Animals make behavioral choices that enhance their energy gain and reduce their risk of becoming prey. Mating behaviors reflect the costs and benefits of parental investment and sexual selection. There are advantages and disadvantages to living in groups.
- Class notes
- • 12 pages •
There are four levels of analysis for questions addressing animal behavior. Animals make behavioral choices that enhance their energy gain and reduce their risk of becoming prey. Mating behaviors reflect the costs and benefits of parental investment and sexual selection. There are advantages and disadvantages to living in groups.

Vertebrates
Land animals had to solve the same problems that plants faced when they moved to land: water conservation, gas exchange, reproduction and dispersal and the fact that water no longer buoyed them up against the pull of gravity The diversification of vertebrates was driven by the evolution of the jaw and limbs. Vertebrates have adapted to life on land as a result of the evolution of tetrapod limbs and an enclosed amniotic egg that allows embryonic development outside a body of water. Mammals and...
- Class notes
- • 11 pages •
Land animals had to solve the same problems that plants faced when they moved to land: water conservation, gas exchange, reproduction and dispersal and the fact that water no longer buoyed them up against the pull of gravity The diversification of vertebrates was driven by the evolution of the jaw and limbs. Vertebrates have adapted to life on land as a result of the evolution of tetrapod limbs and an enclosed amniotic egg that allows embryonic development outside a body of water. Mammals and...

Animal diversity
Kinds of Animals and the evolution, diversity, base body plans including tissues and organs, Porifera, symmetry, the evolution of the nervous system, early development, cnidaria
- Class notes
- • 24 pages •
Kinds of Animals and the evolution, diversity, base body plans including tissues and organs, Porifera, symmetry, the evolution of the nervous system, early development, cnidaria

Core concepts of Fungi
Fungi are eukaryote heterotros that feed by absorption Fungi reproduce both asexually and sexually and disperse by spores Fungi play important roles in nutrient recycling, ecological interactions, and human welfare
- Class notes
- • 13 pages •
Fungi are eukaryote heterotros that feed by absorption Fungi reproduce both asexually and sexually and disperse by spores Fungi play important roles in nutrient recycling, ecological interactions, and human welfare

Plant Origin and Adaptations to land
Adaptations, phylogenetic tree, evidence of plant evolution from green algae, evolutionary trends, transition from water to land, reproduction; for vascular and non vascular plants
- Class notes
- • 10 pages •
Adaptations, phylogenetic tree, evidence of plant evolution from green algae, evolutionary trends, transition from water to land, reproduction; for vascular and non vascular plants
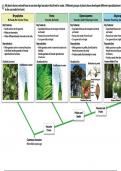
Plant comparison
Demonstrates the developmental specializations of bryophytes, ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms
- Class notes
- • 1 pages •
Demonstrates the developmental specializations of bryophytes, ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms

Alternation of Generations web
Simple web to practice the lifespan/reproduction of a Gametophyte
- Other
- • 1 pages •
Simple web to practice the lifespan/reproduction of a Gametophyte

Evolution of Eukaryotes & Protists
1. The Tree of Life – 3 domains 2. Archaea and bacteria each contributed to the evolution of eukaryotes 3. The endosymbiotic hypothesis proposes that the chloroplasts and mitochondria of eukaryotic cells were originally free-living bacteria. 4. The paradox of sex – why did sex evolve and why is it maintained 5. Evolution of multicellularity – how does complex multicellularity differs from simple multicellularity 6. Diversity in protists including body plan, locomotion, nutrition, inte...
- Class notes
- • 17 pages •
1. The Tree of Life – 3 domains 2. Archaea and bacteria each contributed to the evolution of eukaryotes 3. The endosymbiotic hypothesis proposes that the chloroplasts and mitochondria of eukaryotic cells were originally free-living bacteria. 4. The paradox of sex – why did sex evolve and why is it maintained 5. Evolution of multicellularity – how does complex multicellularity differs from simple multicellularity 6. Diversity in protists including body plan, locomotion, nutrition, inte...

Multicellularity and slime molds
Describes multi-aspects of multicellularity and slime molds including: the phylogenetic tree, social ability, growth, specialization/organization, and evolution
- Class notes
- • 6 pages •
Describes multi-aspects of multicellularity and slime molds including: the phylogenetic tree, social ability, growth, specialization/organization, and evolution

Paradox of Sexual Reproduction
Includes the advantages and disadvantages of asexual/sexual reproduction on cost and effect on genetics.
- Class notes
- • 5 pages •
Includes the advantages and disadvantages of asexual/sexual reproduction on cost and effect on genetics.
